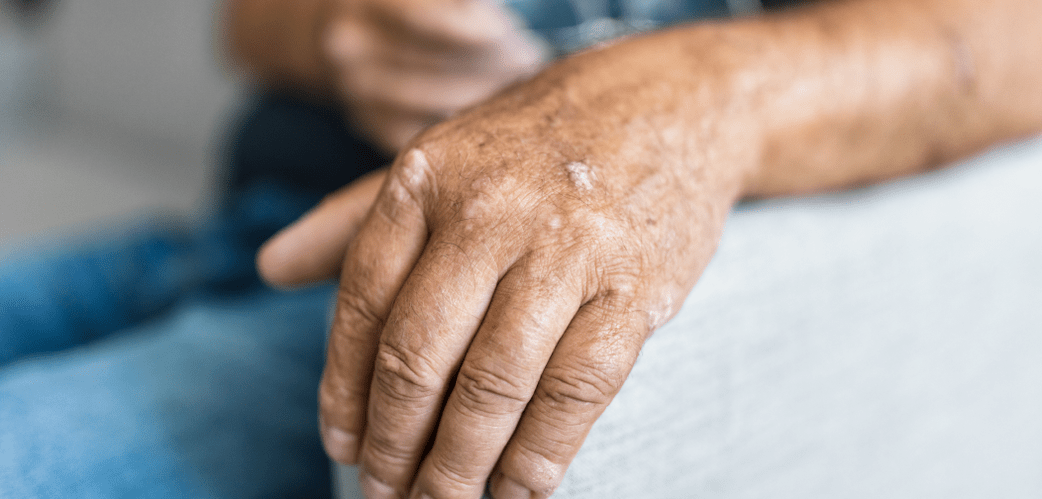
Psoriasis Causes and Risk Factors
autoimmune causes
metabolic effects
- Patients with psoriasis have disordered protein metabolism, reduced albumin content in the blood, increased globulin content, and increased sensitization.
- In fat metabolism, an increase in lipid and cholesterol content in the blood is observed.
- Cutting calories and eating plant-based foods can reduce the activity of psoriasis inflammation.
- Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism almost always occurs.
- The metabolism of vitamins and minerals is also impaired, as shown by the decrease in the levels of vitamins C, A, B6, B12, iron, copper, and zinc in the blood, while the content of vitamin C increases.
Infectious causes
genetic susceptibility
neurogenic causes
endocrine
Symptoms and Characteristics of Psoriasis
- Needle tip (no more than 1 mm in diameter);
- Teardrop shape - (water droplet papules up to 2 mm in size);
- Coin-shaped - (round papules - coin size up to 5 mm).
- Stearic acid stain - if the surface of the papule is scratched;
- Terminal membrane - after clearing the scaly papules, a transparent membrane is visible;
- Blood Dew (Ospitz Phenomenon) – If the integrity of the membrane is compromised, small droplets of blood may appear.
Psoriasis contagious?
Classification and stages of development of psoriasis
- The progressive stage is characterized by the constant formation of new rashes accompanied by severe itching.
- In the quiescent phase, new forms cease to appear and existing forms begin to heal.
- In the degenerative phase, a border appears around the rash and the skin affected by the rash becomes darker due to increased pigmentation.
- Mild, which means no more than 3% of the skin surface is affected.
- Moderate, characterized by 3-10% damage to the skin.
- Severely, the disease affects more than 10%.
Types of psoriasis
Simple (vulgar, plaque)
Elbow psoriasis
guttate psoriasis
Palmoplantar psoriasis
- Fan-shaped patches: Large elements on the palmar and sole surfaces with white scales that merge into fan-shaped patches. This subtype is most common on the hands.
- Round: Ring-shaped scale elements on the palm and sole surfaces.
- Corpus callosum: The growth of rough epithelium that forms a callus.
- Pustular: This is a unique subtype of Barber’s psoriasis on the palms and soles of the feet. The area under the big toe can develop blisters and pustules containing pus, causing severe itching. The ulcers coalesce, then dry and form scabs. Characteristic elements of psoriasis also appear in other parts of the body.
Nail psoriasis
scalp psoriasis
seborrheic psoriasis
psoriasis on face
Genital psoriasis
Why is psoriasis dangerous?
Complications of psoriasis
diagnosis
- Complete blood count, which can detect leukocytosis and anemia in psoriasis.
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) is a protein whose levels may be elevated in systemic inflammatory diseases involving joint damage, but in psoriasis, levels are usually normal.
- The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is also usually normal except in pustular psoriasis and psoriatic erythroderma.
- People with psoriasis may have elevated uric acid levels, which may lead to confusion with gout.
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibodies may be detected during a psoriasis flare-up.
treat
- Topical preparations (topical ointments, petroleum jelly, paraffin, vegetable oils and creams with anti-inflammatory effect, the dosage depends on the nature of the lesion, used daily);
- Lotions and shampoos based on salicylic acid and photosensitizers;
- Oral drugs (retinoids, vitamin D preparations, etc. );
- physical therapy procedures;
- Daily bathing with bath oil, oatmeal infusion, or sea salt can help soften the skin and reduce inflammation caused by psoriasis. It is important to avoid hot water and scrubs and use a moisturizer after bathing;
- Phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light, may also be helpful (to avoid burns);
- Photochemotherapy using medium wave radiation;
- Observe special diets and general regimens.
prevention
Psoriasis Nutrition
- Avoid these foods that your body is allergic to and exclude them from your diet.
- Like fresh fruits, vegetables, berries, lean meats, grilled or boiled meats, and drink plenty of water.
- Avoid the following foods: onions, garlic, radishes, strong tea, coffee, alcohol, sweets, salty and sour foods, and foods that may cause allergic reactions such as oranges, honey, nuts, cocoa and eggs.
- Avoid fatty foods from animal sources.