important!Psoriasis is not contagious to others, but it can cause inconvenience to the patient himself, since the rash that occurs during the disease is not only unsightly but also accompanied by unpleasant itching. In addition, psoriatic arthritis may develop, which can significantly worsen the patient's quality of life.
causes of psoriasis
- Kobner's phenomenon refers to the appearance of a fresh rash at the site of skin irritation in the acute phase of some skin diseases;
- sunburn or other types of burns;
- HIV infection;
- Beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection, leading to punctate psoriasis;
- use of medications (especially beta-blockers, lithium, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors);
- severe emotional stress;
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- Hormonal imbalances, especially in women during menopause and pregnancy;
- Digestive system disorders.
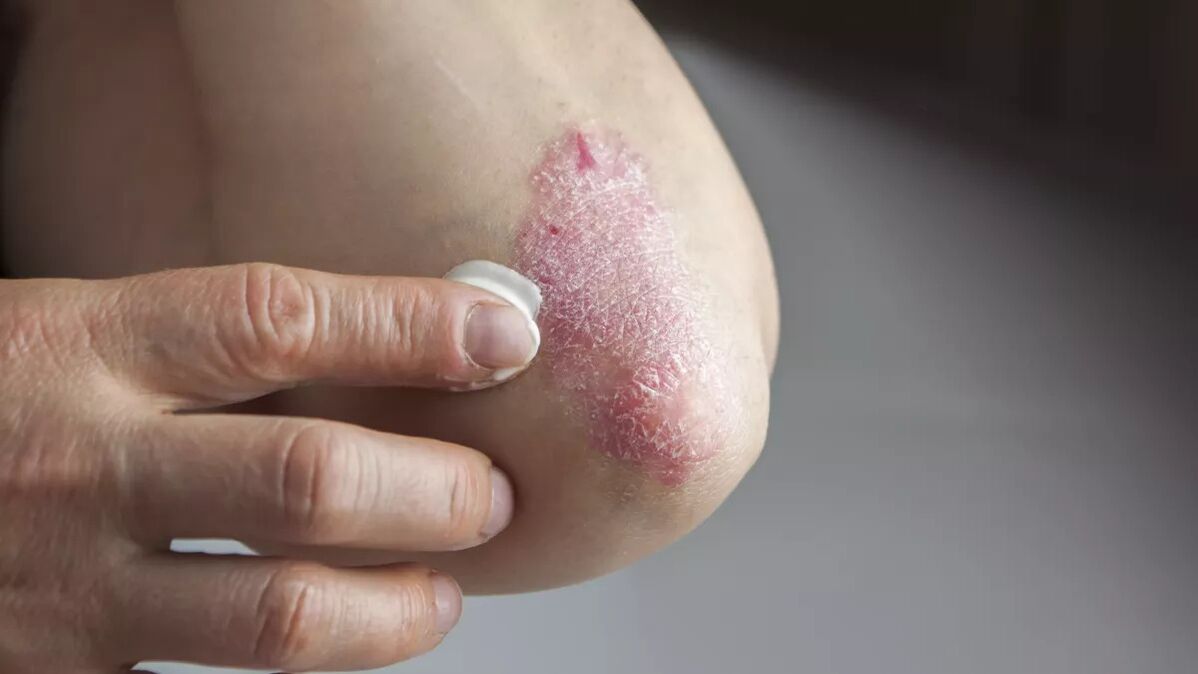
Signs and symptoms of psoriasis
important!Psoriasis does not threaten a patient's life, but it does destroy a patient's self-image. In addition to changes in the patient's appearance, significant time is required to treat the rash and keep clothing and bedding clean, which significantly reduces the patient's quality of life.
Types of psoriasis
- vulgar(common or chronic plaque) psoriasis, a rash that has the appearance of individual plaques covered with silvery flakes of skin. As the disease progresses, plaques may coalesce. Of all subtypes, this type of psoriasis is the most common, accounting for approximately 90% of cases.
- anti psoriasisA rash that occurs in areas of natural folds and may form cracks.
- guttate psoriasisIt is characterized by multiple rashes, 0. 5-1. 5 cm in diameter, often formed after strep pharyngitis.
- palmoplantar psoriasisAppears as plaques on the palms and soles of the feet, which may coalesce.
- Nail psoriasisAffects the nail plate in the form of pinpoint indentations and grooves, causing nail discoloration and thickening. Nail changes caused by psoriasis often resemble changes caused by fungal infections.
- Pustular psoriasisIt is accompanied by the formation of pustules on the palms and soles of the feet, or possibly damage to a finger. There may also be a generalized form.
- Erythrodermic psoriasisPeople with psoriasis plaques develop sudden or gradual redness, while the plaques themselves are mild or non-existent. It usually occurs due to improper treatment of psoriasis vulgaris.
How to diagnose psoriasis
psoriasis treatment
- topical treatment–Ointments and creams work well for treating small areas of localized skin peeling and itching. Hormone ointments, salicylic acid, retinoids, and moisturizers are particularly effective in treating psoriasis on the face and hands.
- medical treatementUse as an additional method to effectively treat psoriasis when ointments do not help. Medications can reduce the inflammatory process, eliminate swelling and itching, and prevent increased activity of skin cells. But it's worth considering that these pills have many side effects (increased fatigue, loss of appetite, high blood pressure). Therefore, it is very important to follow all your doctor's recommendations regarding drug dosage.
- Use when psoriasis is limited to the head and neckMedicated Treatment Shampoo: Antifungal, tar, contains corticosteroids. This shampoo eliminates the pathogens of pathological inflammation, removes scales, relieves itching and burning sensations.
- Therapeutic antihistamine injectionsBlocking severe itching, biologic drugs have beneficial effects on the immune system.